CO as active spectator in hydrocarbon surface chemistry
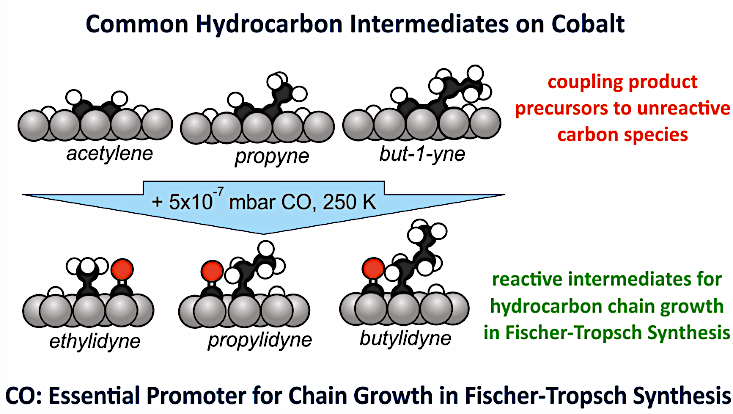
Adsorbed carbon monoxide is of course an essential ingredient in the conversion of syngas (CO+H2) to hydrocarbons, but the CO molecule fulfills another essential role which has until now hardly been appreciated: it enables the growth of hydrocarbon chains on the surface. Without CO, hydrocarbon fragments tend to loose their hydrogen atoms and degenerate to inactive coke, but CO in its immediate surroundings prevents this, and promotes the hydrocarbon species into alkylidynes, which can couple to larger hydrocarbons. The evidence comes from surface science experiments, with thermal desorption and infrared spectroscopy in the lead.
The ECOSS presentation is available for download here.
Published on October 16, 2018